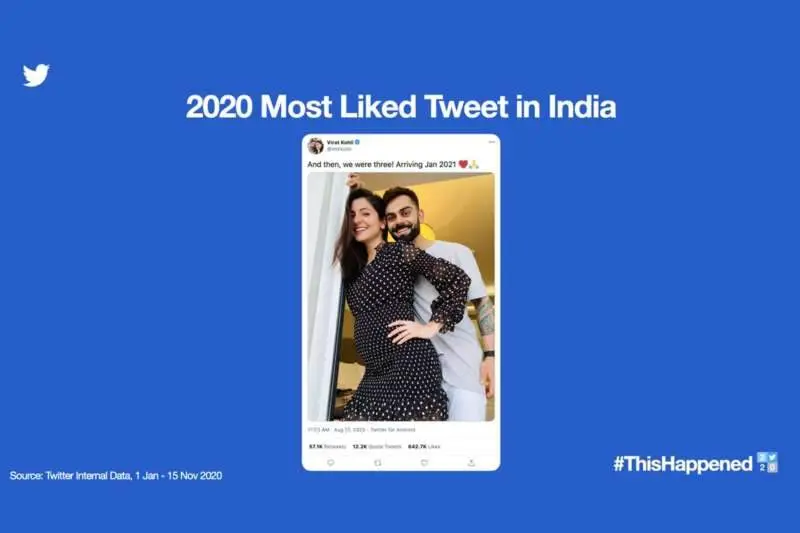
As we brace ourselves to draw curtains on what has been a dramatic year, Twitter has recapped the major happenings in 2020. Sharing insights on what the Twitterati talked about
All posts tagged in 2020
2019 was a great year for movies. Avengers: Endgame broke hell at the box office while Joker awed the critics. Meanwhile, Bollywood remained committed to the trend of biopics, with
The Central Government of India has recently taken the decision of capping the life of commercial vehicles to 20 years. This implies that no commercial vehicles like trucks, taxis, buses
The Road Transport Authority (RTA) has issued cautionary notices to dealers selling BS III vehicles despite the ban imposed on March 31. The central government banned the sale on these
Business Wire IndiaIndia is expected to see a significant uptake in mobile subscriptions, broadband and connectivity by 2020, marking a period of rapid development of the country’s mobile economy, according to a new GSMA Intelligence study published today. The new report, ‘The Mobile Economy: India 2016’, noted that at the end of June 2016, 616 million unique users had subscribed to mobile services in India, making it the second-largest mobile market globally, with almost one billion unique mobile subscribers1 expected by 2020. India also overtook the United States in 2016 to become the world’s second-largest smartphone market with an installed base of 275 million devices. The report forecasts that improving affordability, falling device prices and operator investments in network coverage and quality will help deliver an additional 330 million unique subscribers in India by 2020, lifting the country’s penetration rate to 68 per cent of the population (up from 47 per cent in 2015). India is also seeing an ongoing technology shift to mobile broadband services; the number of 3G/4G mobile broadband connections2 is forecast to reach more than 670 million by 2020, 48 per cent of the total connection base. There will also be an accelerating move to 4G over this period. The number of 4G connections is forecast to grow rapidly, growing from just 3 million at the end of 2015 to 280 million by 2020. In addition, the industry is set to invest heavily, with operator CAPEX growing to $34 billion (INR2.3 lakh crore) for the period 2016 to 2020. “With this report, all signs point to a period of tremendous growth for India’s mobile economy, which will strongly support and enable the government’s ‘Digital India’ initiative aimed at providing broadband connectivity to all,” said Mats Granryd, Director General, GSMA. “To fully realise India’s tremendous market potential, review and reform in key areas, including modernising regulation and long-term planning for spectrum allocation, would accelerate mobile broadband access and adoption across the country.” Reforming Regulation to Accelerate Mobile Broadband Adoption According to the report, with the convergence of technologies and services and the emergence of internet players, India will benefit by modernising regulation to the realities of this new digital ecosystem by thoroughly reviewing the current licensing framework and removing outdated and ineffective regulations. In addition, without sufficient spectrum, mobile services will struggle to meet demand and networks unable to deliver a satisfactory internet experience. The government should continue to free up identified available spectrum for mobile broadband growth. Mobile to Drive Socioeconomic Growth In 2015, India’s mobile industry generated economic value equivalent to 6.5 per cent of the country’s GDP3, a contribution that amounts to more than $140 billion (INR9 lakh crore). The figure accounts for both the direct economic activity generated by mobile operators and the ecosystem of mobile industries in India. This contribution is expected to grow to $210 billion (INR14 lakh core) by 2020. Mobile operators and the ecosystem provided direct employment to approximately 2.2 million people in India, as well as indirectly supporting 1.8 million additional jobs in other industries and sectors that benefit from the activity of the mobile industry, particularly in the direct supply chain. This brings the total impact of the mobile industry to nearly 4 million jobs in 2015. Delivering Digital India through Mobile Broadband Mobile will play a pivotal role in delivering the government’s Digital India vision. As the dominant platform for internet access, given the lack of fixed line infrastructure, high levels of mobile ownership and significant operator investment, mobile has the potential to advance financial access, improve information, and raise productivity throughout India’s economy. As of mid-2016, around 430 million people had access to mobile internet services, a figure that will increase to almost 670 million by 2020, or about half the population. This still lags the regional average of 63 per cent penetration, and the survey found that lack of awareness and locally relevant content are the biggest barriers to internet usage. Financial inclusion is also growing in India. Around 65 per cent of Indian adults have an account with a financial institution, and there is significant room to increase adoption of financial services through mobile technology. Mobile is already the main platform for internet access in India and has brought connectivity to many previously unconnected populations. Digital inclusion can extend various economic and social benefits to previously unconnected populations, fuelling a virtuous circle that reduces poverty, improves infrastructure and services, and further increases internet access and usage,” continued Granryd. To download the new report ‘The Mobile Economy: India 2016’ please visit: http://www.gsma.com/mobileeconomy/india/ -ENDS- About the GSMA The GSMA represents the interests of mobile operators worldwide, uniting nearly 800 operators with almost 300 companies in the broader mobile ecosystem, including handset and device makers, software companies, equipment providers and internet companies, as well as organisations in adjacent industry sectors. The GSMA also produces industry-leading events such as Mobile World Congress, Mobile World Congress Shanghai and the Mobile 360 Series conferences. For more information, please visit the GSMA corporate website at www.gsma.com. Follow the GSMA on Twitter: @GSMA. 1 A unique mobile subscriber represents an individual that can account for multiple mobile connections (SIM cards) 2 Connections defA mobile connection refers to an active SIM card registered with a mobile network, excluding M2M connections. The total number of mobile connections in India reached 1 billion in 2015 and is forecast to rise to 1.4 billion by 2020 3 GDP total includes direct contribution from mobile ecosystem (1.8%);indirect impact (0.4%); and productivity impact (4.3%) View source version on businesswire.com: http://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20161026005570/en/
Business Wire IndiaAt the GSMA Mobile 360 – India conference today, the GSMA announced a further three signatories to the Connected Women Commitment Initiative, which focuses on reducing the gender gap in mobile internet and mobile money services. Aircel, Bharti Airtel and Vodafone have made a commitment to increase the number of women accessing mobile internet services, with additional commitment from Vodafone to grow its base of female mobile money customers. Collectively representing over 100 million customers in these service areas, Aircel, Bharti Airtel and Vodafone now join with other GSMA operator members in committing to connect millions more women in low- and middle-income countries by 2020. GSMA research has shown that in India, there are significant gender gaps in mobile internet and mobile money services, which prevent women from reaping the full benefits of mobile phone ownership. Further, according to the World Bank’s Findex 2014 data1, women in India are 66 per cent less likely to have used and benefitted from mobile money services in the past 12 months. “Addressing the gender gap in mobile phone ownership is an important topic that business leaders and governments will be discussing at the GSMA’s Mobile 360 – India event,” said Mats Granryd, Director General, GSMA. “GSMA research2 shows that South Asia has the highest gender gap globally in mobile phone ownership and that women in India are estimated to be 36 per cent less likely to own a mobile than men, translating into an estimated 114 million fewer women who are benefiting from mobile services. Ensuring digital and financial inclusion for women is essential, because when women thrive, societies and economies thrive.” These latest commitments by three of India’s leading operators build on the 15 million women already benefiting from female-focused services offered by GSMA Connected Women operator partners. Through the Connected Women Commitment Initiative, operators are working to increase the proportion of their female customers, supporting the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), in particular SDG 5, which focuses on achieving gender equality and empowering all women and girls. Operators participating in the Connected Women Commitment Initiative are implementing a range of programmes to address the gender gap, including: increasing the number of female agents; improving the data top-up process to be safer and more appealing to women; and improving digital literacy among women through educational programmes and interactive content. Closing the gender gap in mobile phone ownership and usage in the developing world could unlock an estimated US$170 billion market opportunity for the mobile industry in the period 2015-2020. The Connected Women Commitment Initiative was launched in February 2016 and has now received 30 commitments from 22 operators. In addition to Aircel, Bharti Airtel and Vodafone in India, signatories include Dialog Axiata PLC in Sri Lanka, Digi Telecommunications Sdn Bhd (Digi) in Malaysia, Indosat Ooredoo in Indonesia, Ooredoo Maldives, Orange Mali, Ooredoo Myanmar, Robi Axiata Limited in Bangladesh, Smart Burundi, Smart Tanzania, Smart Uganda, Tigo Chad, Tigo Ghana, Tigo Rwanda Tigo Senegal, Tigo Tanzania, Turkcell and Zantel which totals well over 200 million mobile internet and mobile money customers where a mobile operator has made a commitment (i.e. mobile internet or mobile money). Find out more about the Connected Women Commitment Initiative at http://gsma.com/mobilefordevelopment/the-commitment. -ENDS- Notes to Editors 1 www.worldbank.org/en/programs/globalfindex 2www.gsma.com/mobilefordevelopment/programmes/connected-women/bridging-gender-gap About the GSMA The GSMA represents the interests of mobile operators worldwide, uniting nearly 800 operators with almost 300 companies in the broader mobile ecosystem, including handset and device makers, software companies, equipment providers and internet companies, as well as organisations in adjacent industry sectors. The GSMA also produces industry-leading events such as Mobile World Congress, Mobile World Congress Shanghai and the Mobile 360 Series conferences. For more information, please visit the GSMA corporate website at www.gsma.com. Follow the GSMA on Twitter: @GSMA. View source version on businesswire.com: http://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20161024005921/en/